Agile methodologies have transformed the way software development and businesses operate, revolutionizing project management practices. At the center of this transformation is the role of an Agile Business Analyst.
In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of this vital role, exploring their responsibilities, required skills, and the significance of their contribution to today’s dynamic business world.

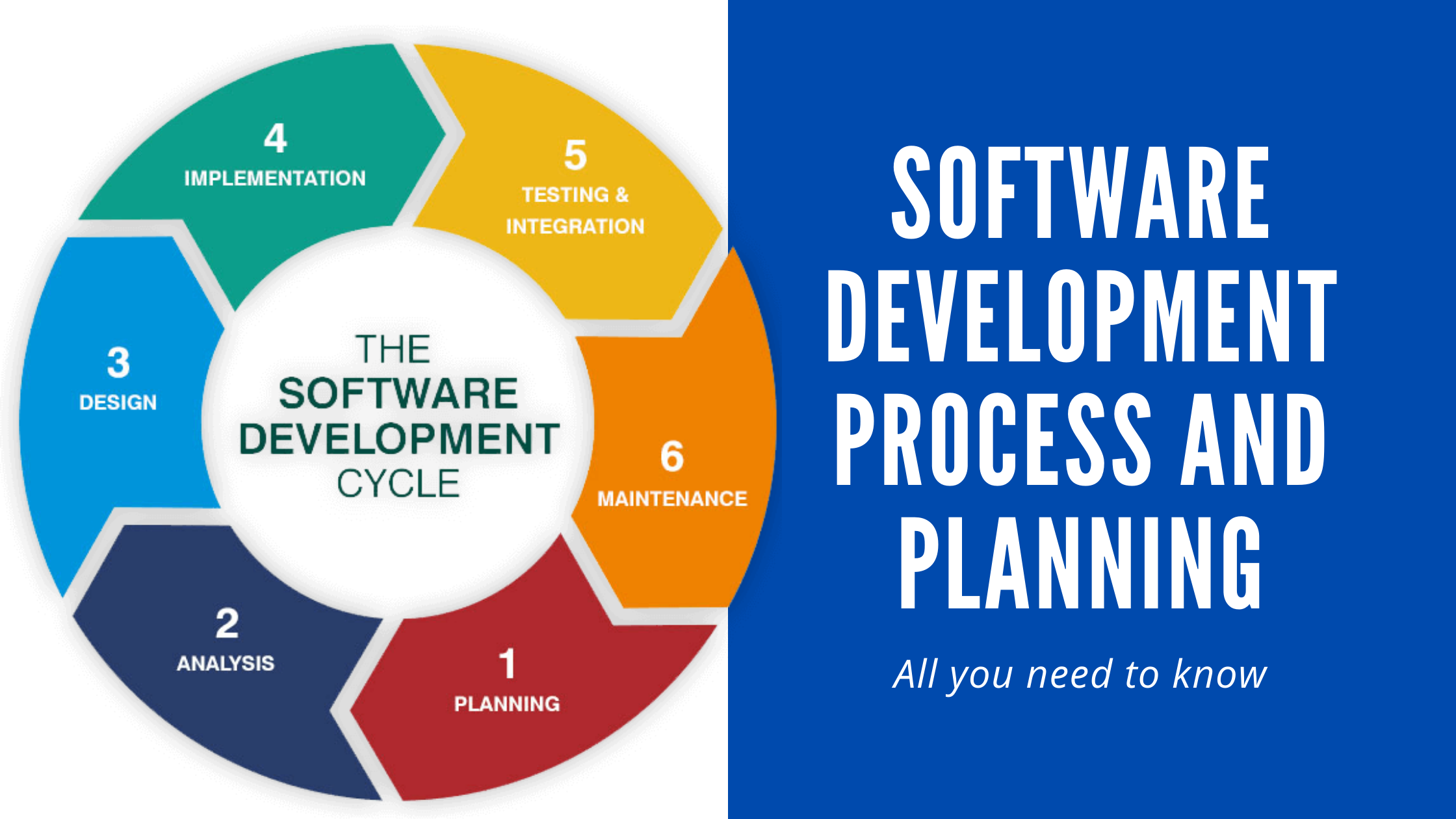
An Overview of Agile Project Management
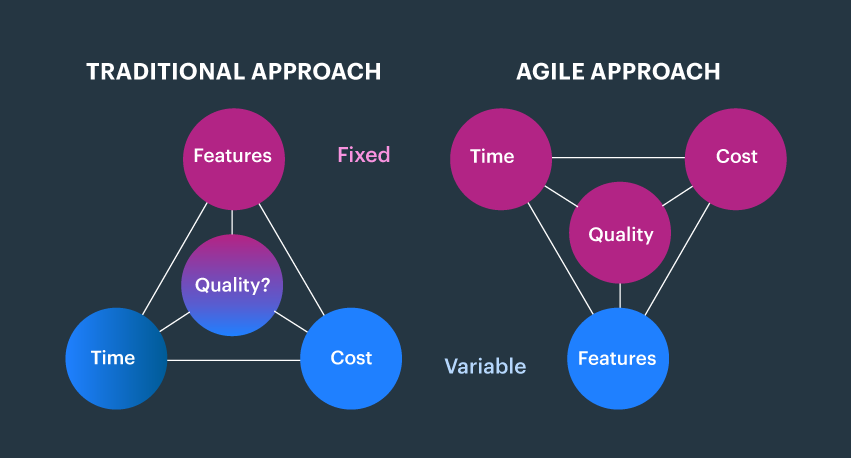
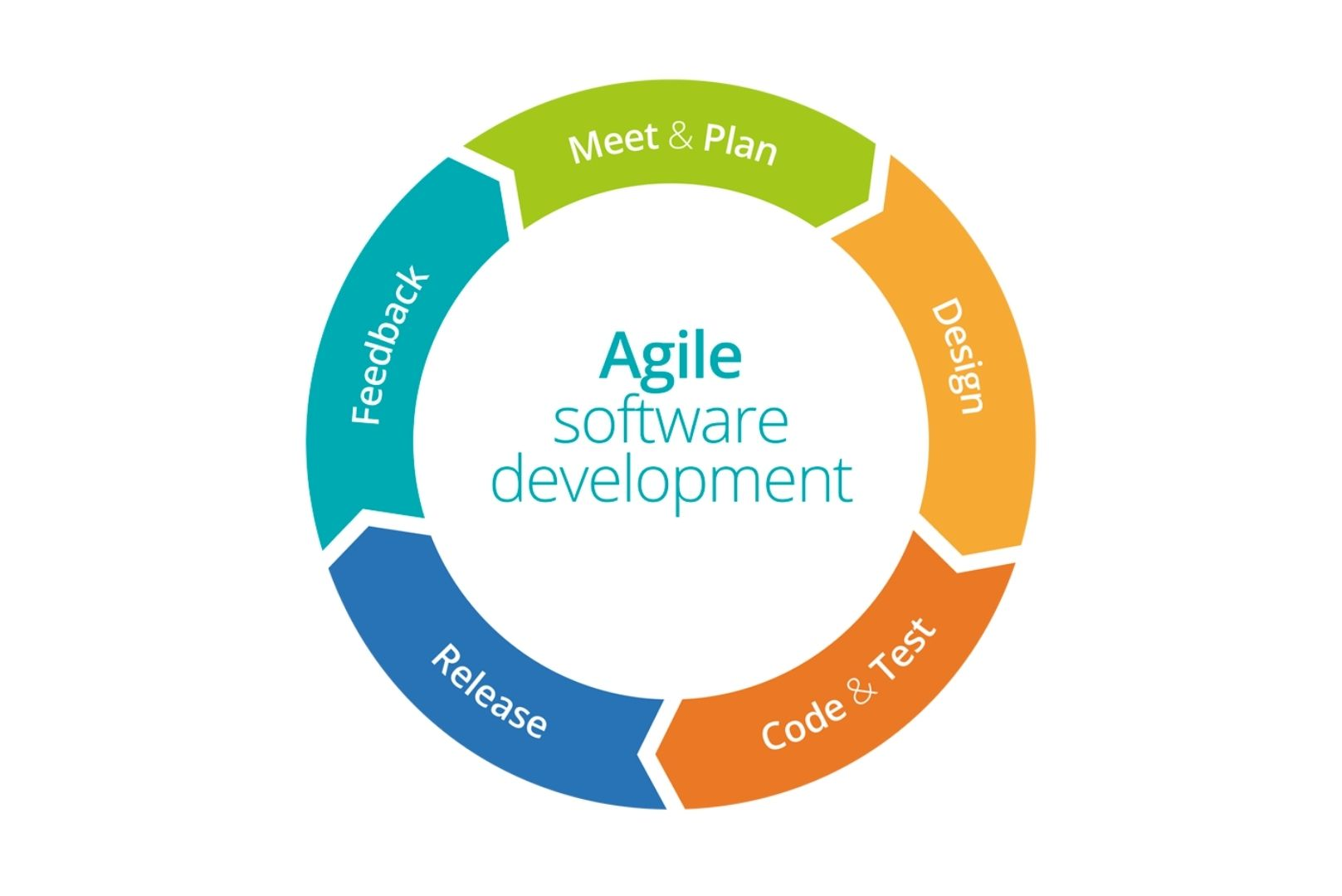
Dynamic Project Coordination is an adaptable and evolving methodology for overseeing projects that underscore pliancy, cooperation, and offering worth to clients. Its roots can be traced back to the software development sector, but it has garnered widespread adoption in diverse domains for its efficacy in managing intricate and rapidly fluctuating circumstances. Here’s a general outline of Dynamic Project Coordination:
Iterative and Incremental: Every Agile project is divided into small iterations, typically called “sprints” in Scrum, where a defined set of features or functionalities is developed and delivered. Each sprint results in a potentially shippable product increment. The project evolves through multiple iterations, with feedback from stakeholders influencing subsequent development.
Customer-Centric Approach: The focus of Agile Project Management is on delivering value to the customer. Customer feedback is continually solicited and integrated into the project, allowing for adaptive and customer-driven development.
Empowering Teams: Agile Project Management empowers cross-functional teams to self-organize and make decisions collaboratively. Team members work together closely, breaking down silos and improving communication and coordination.
Flexible and Adaptive: Agile embraces change and responds to new requirements or market conditions by adjusting project scope and priorities at the end of each iteration. This adaptability ensures that the project remains relevant and aligned with business needs.
Roles and Ceremonies: Agile Project Management typically involves key roles such as Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team. Ceremonies, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, provide the framework for team collaboration and communication.
User Stories and Backlog: Requirements are captured in the form of user stories, which represent features or functionalities from the perspective of end-users. The product backlog is a prioritized list of user stories, which guides the team’s work during each iteration.
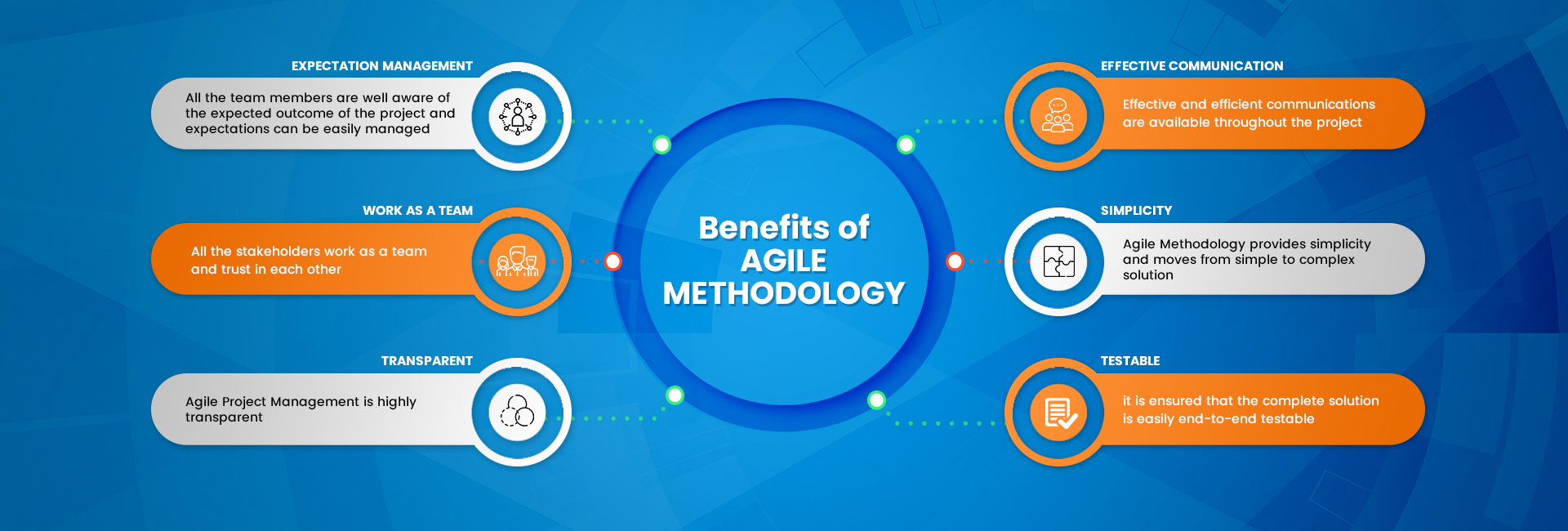
Continuous Improvement: Agile Project Management promotes a culture of continuous improvement. Teams regularly reflect on their processes and performance during retrospectives, identifying areas for enhancement and making adjustments to improve productivity and effectiveness.
Transparency and Visibility: Agile Project Management emphasizes transparency in all aspects of the project. Progress, challenges, and decisions are made visible to all stakeholders, ensuring shared understanding and alignment.
Measuring Progress: Progress in Agile Project Management is measured through the delivery of working increments at the end of each iteration. Velocity, a measure of the team’s output, is often used to estimate how much work can be completed in future iterations.
Embracing Feedback: Frequent feedback loops are integral to Agile. Regularly seeking feedback from stakeholders and end-users helps validate assumptions and ensures the delivered product meets customer expectations.
Agile Project Management methodologies, such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean, provide frameworks for implementing these principles effectively. The goal is to maximize customer value, increase team productivity, and respond swiftly to change, resulting in successful project outcomes and satisfied stakeholders.
Who is an Agile Business Analyst?
In the large and continuously evolving world of agile project management, the role of an Agile business analyst is of paramount importance and pivotal. Having said that, you can never have a good grasp of this position, unless you acquire a fair understanding of Agile methodologies.
Understanding Agile Methodology
Agile project management focuses on adaptability and iterative development. It allows teams to respond quickly to changing requirements, ensuring the final product aligns with the ever-evolving needs of the business and its customers. Agile promotes collaboration, frequent feedback, and continuous improvement throughout the development process.

Enabling Effective Agile Principles
An Agile Business Analyst is an essential enabler of Agile principles. They act as a bridge between stakeholders and the development groups and team, ensuring that everyone involved understands the project objectives and works together cohesively. By facilitating effective communication, an Agile Business Analyst fosters an environment where all team members have a shared understanding of the project’s goals and priorities.
Roles and Responsibilities of an Agile Business Analyst
For any Agile project management system to work smoothly, the roles and responsibilities of an Agile business analyst must be clearly defined. The roles and responsibilities of an Agile Business Analyst encompass a wide range of tasks throughout the Agile project lifecycle. Here are some key roles and responsibilities:
Collaborating with the Agile Team
An Agile Business Analyst is an integral part of the Agile team. They collaborate closely with the product owner, development team, and other stakeholders. By fostering open communication and transparency, they ensure that all team members are aligned and working towards the common goal of delivering value to the business.
Analyzing Business Needs and Providing Solutions
One of the primary responsibilities of an Agile Business Analyst is to identify and analyze the business needs behind a project. They engage with stakeholders to understand their requirements and concerns thoroughly. Based on this understanding, the Agile Business Analyst translates these needs into actionable solutions that can be implemented by the development team.
Understanding the Business Domain
To be effective, an Agile Business Analyst must possess in-depth knowledge of the business domain they are working in. They need to understand the industry, market trends, customer preferences, and the competitive landscape. This understanding allows them to make informed decisions and contribute valuable insights during project discussions.
Stocking and Grooming the Product Backlog
An Agile Business Analyst actively maintains and grooms the product backlog, which is a prioritized list of features, user stories, and tasks that need to be addressed during the project. By organizing and managing the backlog, they ensure that the team is continuously working on the most valuable tasks and meeting business objectives.
Guiding the Team and Prioritizing Tasks
An Agile Business Analyst plays a critical role in guiding the development team throughout the project. They help the team see the big picture and understand how their individual tasks contribute to the overall success of the project. By prioritizing tasks and features based on business value, an Agile Business Analyst ensures that the team remains focused on delivering high-impact results.
Being a Business Advisor
An Agile Business Analyst is not just a technical expert; they also act as a business advisor. They provide valuable guidance and recommendations to stakeholders and the development team, considering both technical feasibility and business value. This advisory role is crucial in making well-informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle.

Documenting Processes and Requirements
In Agile projects, clear and concise documentation is essential. An Agile Business Analyst takes the lead in documenting project requirements, user stories, acceptance criteria, and other relevant information. Well-documented processes ensure that everyone involved understands the project’s scope and objectives, reducing the chances of miscommunication or misunderstandings.
Ensuring Project Goals are Met
As a key member of the Agile team, an Agile Business Analyst is committed to ensuring that the project goals are achieved. They continuously assess project progress, identify potential risks, and propose adjustments when needed. Their focus on meeting project goals drives the team towards successful project delivery.
Skills Required to be an Agile Business Analyst
For a better performance in Agile project management and to excel as an Agile Business Analyst, certain skills are essential to effectively perform the roles and responsibilities in Agile project management. Here are some crucial skills required:

Detailed Business Knowledge
A comprehensive understanding of business processes, industry-specific requirements, and market dynamics is essential for an Agile Business Analyst. This knowledge allows them to interpret and prioritize project requirements in alignment with the business objectives.
Communication Skills
Clear and effective communication is fundamental to the success of an Agile Business Analyst. They must communicate with various stakeholders, such as product owners, developers, testers, and end-users. Effective communication ensures that everyone involved in the project understands the requirements, progress, and changes.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Agile project management is characterized by its dynamic nature. An Agile Business Analyst must be adaptable and open to change. They should be able to respond to shifting priorities, emerging risks, and evolving business needs.
Proficiency in Agile Tools and Techniques
An Agile Business Analyst should be well-versed in Agile tools and techniques commonly used in Agile project management. These tools may include collaboration platforms like Jira or Trello, data visualization tools, and Agile-specific metrics and charts.
Anticipation
Anticipating potential challenges and opportunities is a valuable skill for an Agile Business Analyst. By staying ahead of potential issues, they can proactively address risks and ensure smooth project execution.
Problem-solving Skills
Agile Business Analysts must be skilled problem solvers. They encounter complex challenges during projects and are responsible for finding innovative and practical solutions that align with the Agile principles.
Critical Thinking Abilities
Critical thinking is crucial for analyzing project management requirements, identifying dependencies, and making data-driven decisions. An Agile Business Analyst employs critical thinking to assess the impact of various decisions on the project outcomes.
Good Knowledge of Analytics
Analytics plays a significant role in Agile projects, where data-driven insights inform decision-making. An Agile Business Analyst should have a good understanding of data analysis techniques and tools to leverage the available data effectively.
Strong Relationship-building Skills
Building positive relationships with stakeholders, team members, and customers fosters collaboration and trust. Agile Business Analysts leverage their relationship-building skills to create a supportive and productive team environment.
Process Modeling Skills
Process modeling involves visually representing workflows and business processes. Agile Business Analysts use this skill to enhance understanding and streamline project processes, leading to improved project management and better outcomes.

How to Become an Agile Business Analyst from a Traditional BA?
Transitioning from a traditional Business Analyst (BA) to an Agile Business Analyst involves acquiring new skills, adopting a different mindset, and embracing Agile principles and methodologies. Here’s a step-by-step guide to becoming an Agile Business Analyst:
Learning from Agile Development Teams
Transitioning from a traditional BA to an Agile Business Analyst involves immersing oneself in Agile development teams. By observing Agile practices in action, a traditional BA can learn the nuances of Agile project management and collaboration.
Attending Agile Training Courses and Workshops
Formal training in Agile principles and practices is an excellent way for a traditional BA to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills. Attending workshops and courses conducted by experienced Agile practitioners provides valuable insights.
Reading Books and Articles on Agile Methodology
Staying informed about Agile methodologies and best practices through reading books and articles expands a traditional BA’s understanding of Agile project management.
Formal Training in Agile Methodologies
Formal certifications, such as Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) or Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO), provide a structured approach to learning Agile methodologies and bolster a traditional BA’s transition to an Agile Business Analyst.
Relevant Industry Experience
Real-world experience in Agile project management allows a traditional BA to put their knowledge into practice and develop a deeper understanding of Agile project dynamics.

Qualifications of an Agile Business Analyst
The qualifications of an Agile Business Analyst typically involve a combination of educational background, professional certifications, and relevant experience. While specific qualifications may vary depending on the organization and the complexity of the projects, here are common qualifications sought for Agile Business Analyst roles:
Analytical, Problem-solving, and Communication Skills
The trio of analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills are foundational for an Agile Business Analyst. These skills enable them to dissect complex situations, propose solutions, and effectively convey ideas to various stakeholders.
Understanding Business and Technical Requirements
An Agile Business Analyst should have the ability to comprehend both business and technical requirements. This understanding enables them to align project objectives with business goals while also considering the technical feasibility of proposed solutions.
Deep Knowledge of Agile Methodology and Principles
Mastery of Agile methodologies, principles, and best practices is critical for an Agile Business Analyst to steer projects in the right direction. A deep understanding of Agile concepts ensures that they can apply Agile principles effectively.
Postgraduate Degree in Computers or Business Discipline
A postgraduate degree in computers or a business discipline can provide an excellent academic foundation for an Agile Business Analyst’s career.
Membership in Agile Organizations
Joining Agile organizations and communities allows an Agile Business Analyst to stay connected with the latest industry trends, share insights, and learn from peers.
Professional Certifications
Obtaining professional certifications, such as Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) or Project Management Institute – Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP), validates an Agile Business Analyst’s expertise and enhances their credibility.

Agile Business Analyst Salary Overview
The salary of an Agile Business Analyst varies based on experience, qualifications, and the complexity of projects they handle. Generally, experienced Agile Business Analysts command higher salaries due to their expertise.
Additionally, salaries for Agile Business Analysts can differ significantly based on the region or city they work in. Cities with higher living costs and a strong demand for Agile professionals tend to offer higher compensation packages.
Roles of an Agile Business Analyst as a Business Advisor and in Documenting Processes
As an Agile Business Analyst, the role involves acting as both a Business Advisor and a Documenter of Processes:
Advising Businesses on Utilizing Agile Methodologies Effectively
An Agile Business Analyst is not just a technical expert but also a trusted advisor. They collaborate with stakeholders, understand their pain points, and offer tailored solutions to help businesses make the most of Agile practices.
Communicating with Stakeholders and Agile Delivery Teams
Clear and effective communication is fundamental to the Agile Business Analyst’s role. They serve as the conduit between stakeholders and the Agile delivery team, ensuring that requirements are well-understood and implemented accordingly.
Documenting the Software Development Life Cycle Phases
Thorough documentation is crucial for the success of Agile projects. An Agile Business Analyst maintains accurate records of the software development life cycle, including requirements, user stories, sprint planning, and retrospectives.
Ensuring Compliance with Organizational Standards
In addition to managing project documentation, an Agile Business Analyst ensures that project processes align with organizational standards, guidelines, and best practices.
Tools for Agile Business Analysts
Agile Business Analysts utilize a range of helpful tools and software to enhance Agile project management and collaboration within Agile projects. These tools are specifically designed to facilitate Agile methods and enable seamless communication among team members. Here are some popular tools commonly used by Agile Business Analysts:
Jira:
Jira is one of the most widely used Agile project management tools for Agile teams. It provides a centralized platform for planning, tracking, and managing tasks and user stories. Agile Business Analysts can create and prioritize user stories, assign tasks to team members, and track progress using Jira’s boards, such as Scrum or Kanban boards. Jira’s extensive reporting and analytics capabilities allow teams to gain valuable insights into project performance and identify areas for improvement.
Trello:
Trello is a user-friendly, visual Agile project management tool that Agile Business Analysts often use to manage tasks and workflows. It uses boards, lists, and cards to represent project stages and individual tasks. Agile teams can easily collaborate by moving cards across lists to indicate progress. Trello’s simplicity and flexibility make it a popular choice for teams looking for a lightweight Agile project management solution.
Pivotal Tracker:
Pivotal Tracker is another tool designed specifically for Agile software development. It allows Agile Business Analysts to create and prioritize stories, estimate work, and manage iterations using a drag-and-drop interface. Pivotal Tracker provides visibility into the team’s velocity and helps maintain a consistent pace of delivery throughout the project.
Confluence:
Confluence is a collaborative wiki tool that enables teams to create, share, and organize project documentation and knowledge. Agile Business Analysts can use Confluence to maintain project requirements, user stories, meeting notes, and other essential project information. It promotes transparency and ensures that all team members have access to up-to-date project documentation.
Miro:
Miro is an online whiteboard platform that fosters remote collaboration among Agile teams. Agile Business Analysts can use Miro to conduct virtual workshops, brainstorming sessions, and retrospectives. The platform allows team members to create and share visual diagrams, charts, and sticky notes, enhancing the visualization and understanding of complex concepts.
Slack:
Slack is a popular team communication tool that fosters real-time communication among Agile team members. Agile Business Analysts can create channels for specific topics, projects, or teams, enabling instant messaging, file sharing, and integrations with other tools. Slack promotes quick and efficient communication, making it easier for teams to stay connected and resolve issues promptly.
Facilitating Collaboration and Generating Examples
Agile Business Analysts employ various techniques to facilitate collaboration within Agile project management. They conduct workshops, brainstorming sessions, and daily stand-ups to foster communication and teamwork among team members.
Additionally, to enhance project understanding, they use real-life examples and use cases. By presenting relatable scenarios, Agile Business Analysts help team members better grasp complex project requirements and deliverables, promoting effective collaboration and successful project outcomes.

Transferring Knowledge and Building a Career
To build a successful career as an Agile Business Analyst, professionals should employ various strategies for effective knowledge transfer within their teams and across the organization. This ensures the sharing of best practices and helps new team members quickly adapt to the Agile environment.
By continuously learning, networking with industry professionals, and actively seeking opportunities to work on diverse and challenging projects, aspiring Agile Business Analysts can pave the way for a rewarding and fulfilling career.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Agile Business Analysts play a pivotal role in driving successful Agile projects by understanding business needs, facilitating collaboration, and providing valuable insights, contributing significantly to project success.
A career as an Agile Business Analyst offers exciting opportunities to work on cutting-edge projects, collaborate with diverse teams, and make a lasting impact in the world of software development and business. Aspiring professionals should embrace this dynamic and rewarding path with enthusiasm and dedication.
FAQs
What is the role of a Business Analyst in Agile project management?
The role of a Business Analyst in Agile project management is to act as a liaison between business stakeholders and development teams. They gather and analyze requirements, ensuring that project objectives align with business needs. They play a crucial part in facilitating collaboration, promoting effective communication, and adapting to changing requirements throughout the project lifecycle.
How does a Business Analyst contribute to a project?
A Business Analyst contributes to a project by understanding the business’s goals, needs, and requirements and translating them into clear and actionable tasks for the development team. They ensure that the project stays on track, meets the stakeholders’ expectations, and provide valuable insights to optimize processes and deliver value to the organization.
What is BA’s role in Agile Scrum?
In Agile Scrum, a Business Analyst collaborates closely with the product owner and development team. Their role involves gathering and refining user stories, ensuring they are well-defined and actionable. They participate in sprint planning, backlog grooming, and daily stand-ups, actively engaging with team members to address questions and support the delivery of a successful product increment.
What are the benefits of Agile business analysis?
The benefits of Agile business analysis include better alignment with business goals and customer needs, improved collaboration and communication between stakeholders and development teams, quicker adaptation to changing requirements, and the ability to deliver value early and frequently. Agile business analysis also promotes continuous improvement and fosters a culture of innovation, leading to more successful and customer-centric projects.



