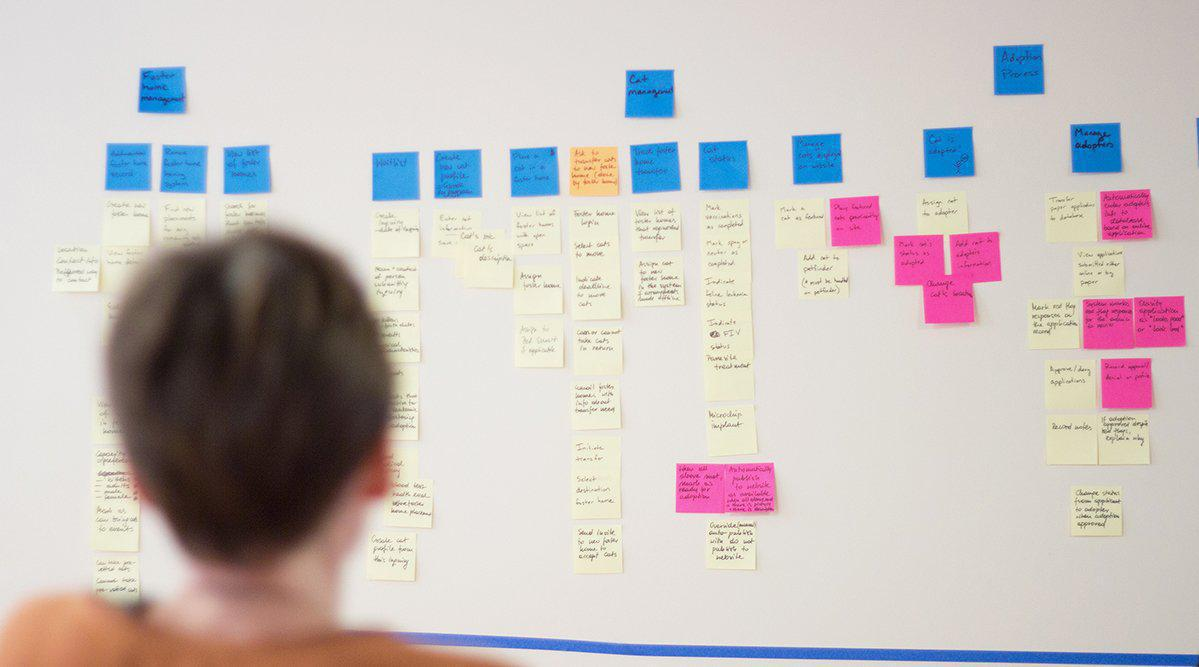
User Story Mapping is a powerful technique used by Agile organizations to create a visual representation of product features and user interactions. It allows teams to collaboratively prioritize work, focus on user value, and deliver delightful customer experiences.

In this comprehensive article, we will explore the ins and outs of User Story Mapping, its purpose, benefits, and the step-by-step process to implement it effectively.
Definition of User Story Mapping
User Story Mapping is a technique that helps product teams create a dynamic outline of user interactions and product features. It involves breaking down complex ideas into smaller user stories, which are then prioritized to create a roadmap for product development.
Purpose and Benefits of User Story Mapping
The primary purpose of User Story Mapping is to build a shared understanding of the product vision and prioritize work that aligns with user value. It benefits the team in numerous ways, including improved communication, early delivery of new value, and clear product goals.

Overview of User Story Mapping
This visual technique involves creating a visual representation of user activities, breaking them down into smaller stories, and prioritizing them to form a coherent product roadmap. This approach helps teams maintain focus on user value throughout the development process.
How User Story Mapping Works
User Story Mapping works by creating a visual representation of the product’s user interactions and features. It allows teams to validate and prioritize work, providing an alternative to traditional backlog approaches. Let’s dive into the details of how it all comes together.
Creating a Dynamic Outline of User Interactions
User Story Mapping starts with creating a dynamic outline of user interactions, also known as the user journey. This involves understanding the target audience and defining user personas to tailor the product experience.
Using User Stories to Validate and Prioritize Work
User stories act as building blocks for the user journey. They are small, manageable units of work that represent user value. By using user stories, teams can validate their assumptions and prioritize work based on user needs.
Alternative to Traditional Backlog Approaches
User Story Mapping provides an alternative to the traditional flat backlog, which often lacks context and shared vision. By visualizing the user journey, teams can better understand the product’s flow and interdependencies.

Limitations of a Traditional Flat Backlog
Traditional backlogs may suffer from a lack of context and user-centric focus. This can lead to inefficient prioritization, resulting in features that do not align with user value.
Challenges with User Story Prioritization
Prioritizing user stories can be challenging, especially when there are conflicting perspectives within the team. Without a clear understanding of user value, teams may struggle to deliver a compelling product experience.
Lack of Context and Shared Vision
Without a shared vision, the development team may struggle to deliver a cohesive product. This approach helps align all team members around a common goal, fostering a sense of shared ownership.

User Story Mapping Process
The process in which we create user story maps involves several steps, each contributing to the overall success of the technique. From framing the problem to planning sprints and releases, let’s explore the entire process.
Framing the Problem and Goal-First Approach
The first step in Story Mapping is framing the problem and defining clear goals. A goal-first approach ensures that the team stays focused on the overall objectives throughout the process.
Understanding the Target Audience and User Personas
To create a successful user story map, it’s essential to understand the target audience and develop user personas. This step ensures that the product addresses real user needs and pain points.
Mapping User Activities (Themes/Functions)
User activities, also known as themes or functions, represent the different tasks and interactions users will perform with the product. Mapping these activities is a crucial step in creating a comprehensive user journey.
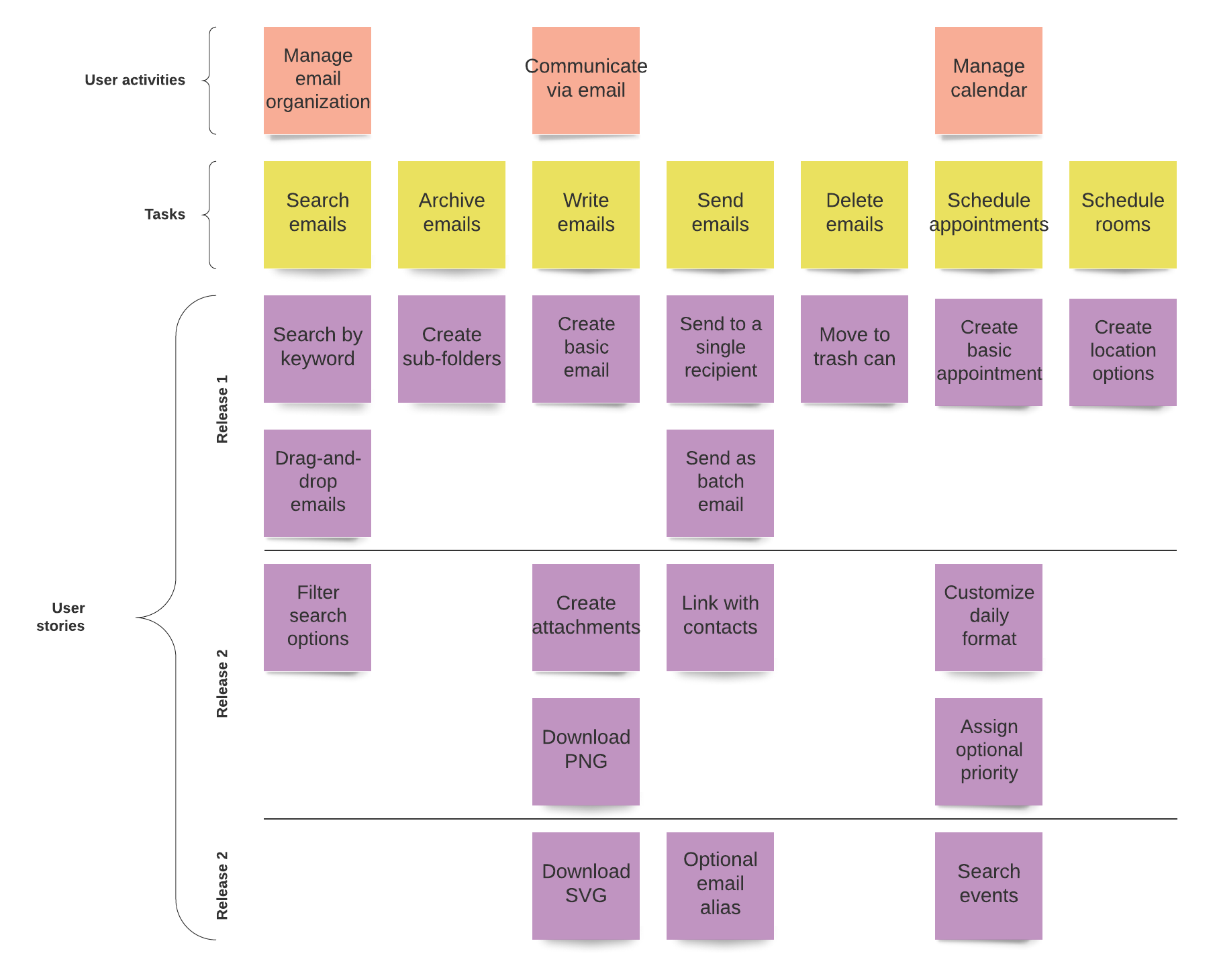
Breaking Down Activities into Smaller User Stories
Once the activities are mapped, the next step is to break them down into smaller, manageable user stories. These stories represent the individual features and functionalities of the product.
Prioritizing Stories and Mapping User Flow
With a set of user stories in place, the team can prioritize them based on user value and feasibility. Mapping the user flow helps visualize how users will interact with the product.
Identifying Gaps, Risks, Dependencies, and Technical Requirements
While creating the user story map, it’s essential to identify any gaps, risks, or dependencies that might impact the product’s development. Technical requirements are also considered during this stage.
Planning Sprints and Releases for Delightful Customer Experience
Once the user story map is complete and prioritized, the team can plan sprints and releases to deliver a delightful customer experience in a structured manner.
Pre Phase: Gather Documents and Choose the Mapping Tool
Before beginning the actual mapping process, it’s essential to gather all necessary documents and choose the right mapping tool for collaboration.
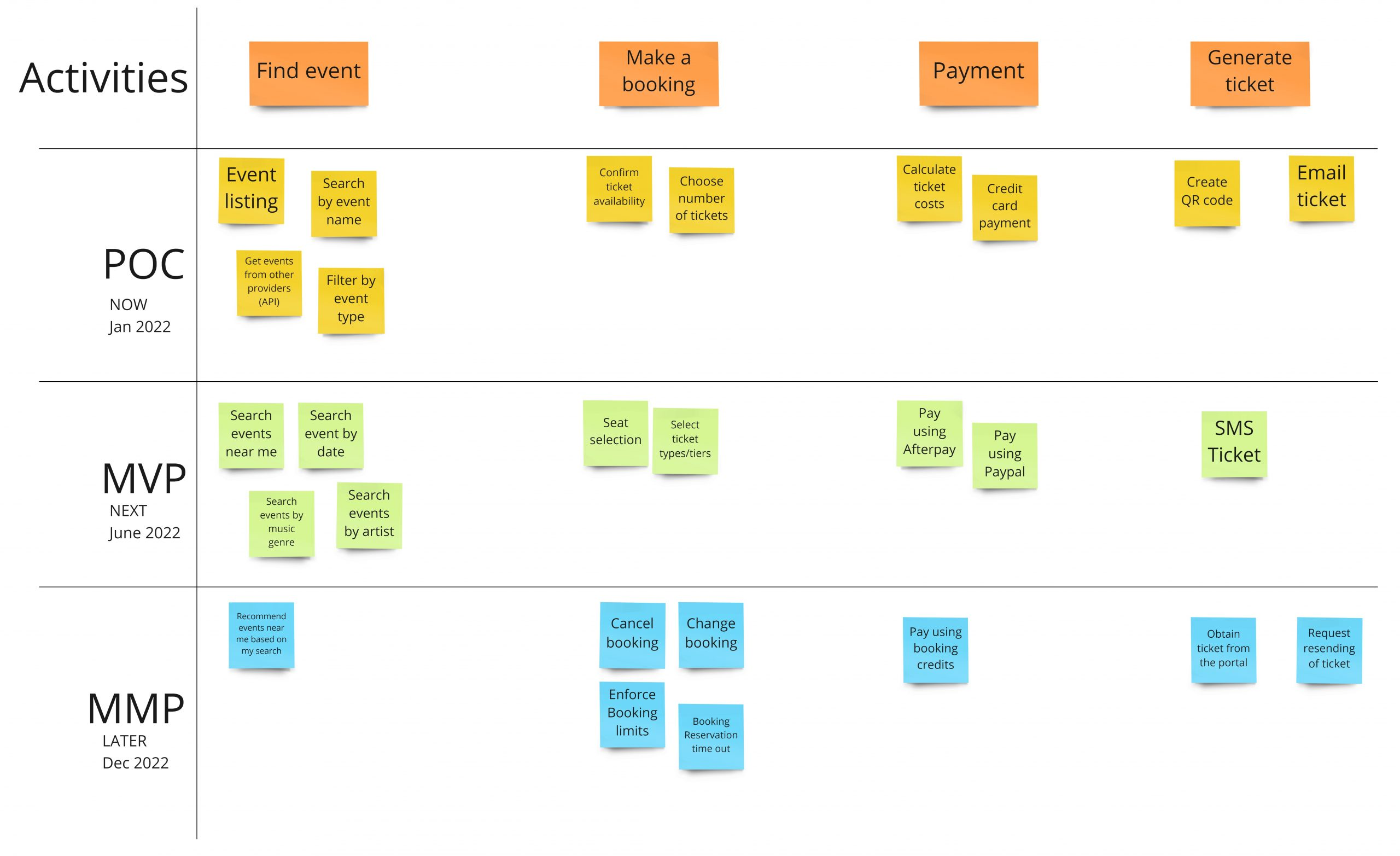
Step 1: Select Members of the Story Mapping Team
A cross-functional team consisting of members from engineering, UX, product, and other relevant departments should be selected for the story mapping process.
Step 2: Set the Frames of the User Story Map and Define Goals
The team sets the frames of the user story format, defining the scope and boundaries of the project. Clear goals are established to drive the mapping process.
Step 3: Implement User Personas
User personas are created and implemented to ensure a user-centric approach throughout the mapping process.
Step 4: Appoint the Meeting and Onboard Participants
The team appoints a meeting facilitator and ensures that all participants are onboarded and aware of the mapping process.
Step 5: Conduct the Workshop and Build the Backbone
The team conducts a workshop to build the backbone of the user story maps, capturing the high-level user activities.
Step 6: Write User Stories and Decompose Epics
User stories are written based on high-level activities, and epics are decomposed into smaller, more manageable stories.
Step 7: Prioritize Stories and Outline MVP
The team prioritizes the user stories based on user value and outlines the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to deliver early value.
Step 8: Arrange Remaining User Stories and Additional Sections
The remaining user stories are arranged in the user journey, and additional sections are added to capture any remaining details.

User Story Maps Maintenance Tips
Tips for maintaining and updating the user story map are provided to ensure its relevance and usefulness throughout the product’s lifecycle.
Benefits of User Story Mapping
User Story Mapping offers numerous benefits that contribute to successful product development and team collaboration. Let’s explore these advantages in detail.

Focusing on User Value
User Story Mapping keeps the team centered on user value by visually representing the user journey and aligning feature prioritization with user needs. This ensures that the development efforts are directed towards creating maximum value for the end-users.
Prioritizing the Right Work for Complete Product Experience
Breaking down the product into smaller, manageable user stories and prioritizing them enables the team to focus on developing the essential features required for a complete and satisfactory product experience. This approach helps avoid wasting resources on less critical functionalities.
Driving Clear and Well-Sized Requirements
Through User Story Mapping, teams can articulate clear and well-sized requirements. The concise user stories are easier to manage, understand, and implement, leading to efficient development cycles.
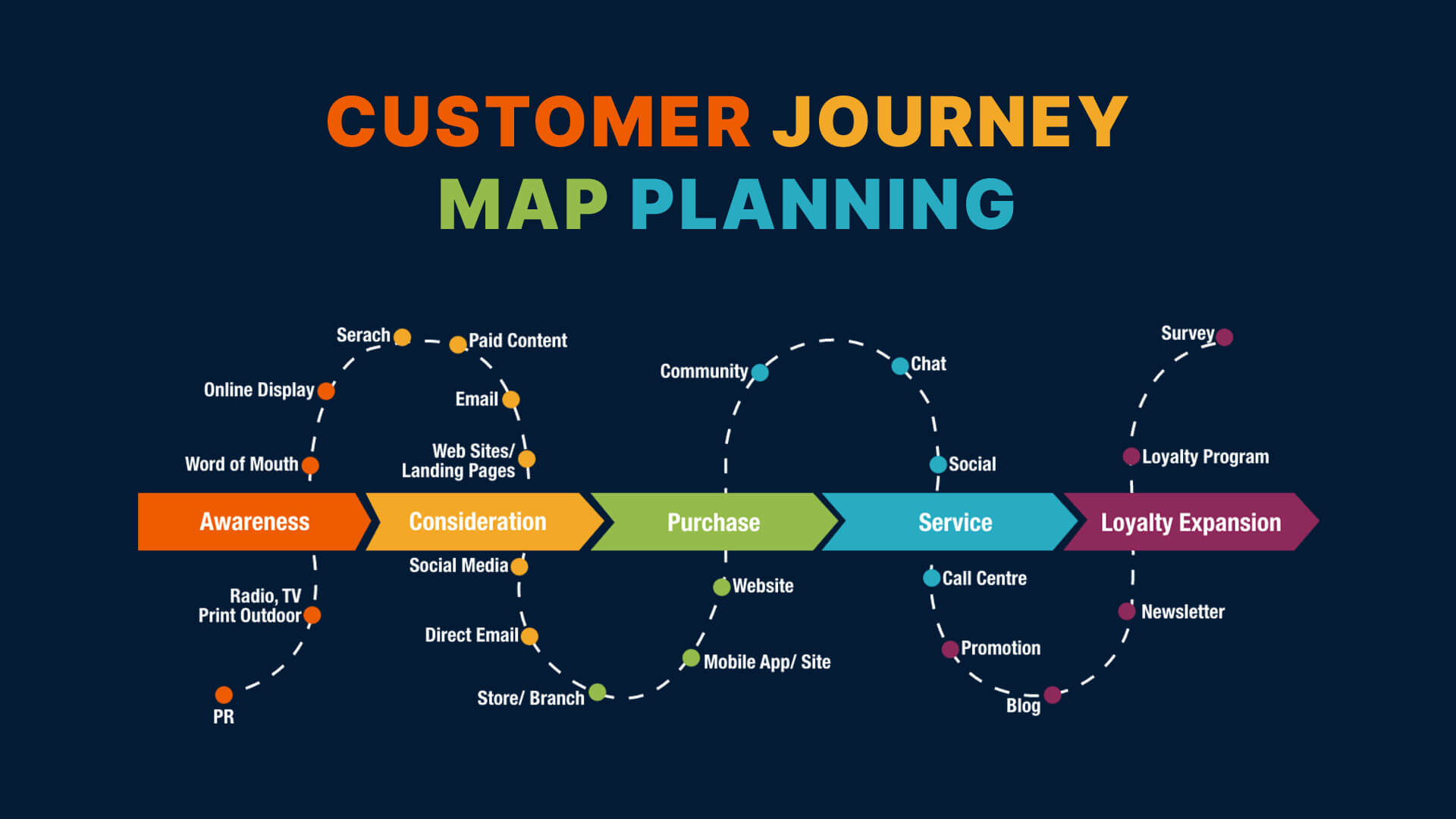
Delivering New Value Early and Often
By emphasizing the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) and delivering it early, Story Mapping allows teams to release valuable features sooner, fostering continuous feedback and iterative improvements. This iterative approach accelerates the development cycle and ensures that user feedback is quickly integrated into the product.
Exposing Risks and Dependencies for Successful Delivery
User Story Mapping helps teams identify potential risks and dependencies early in the development process. By addressing these challenges proactively, teams can reduce project setbacks and improve the chances of successful product delivery.
Building Team Consensus and Shared Understanding
The collaborative nature of User Story Mapping encourages team members to actively participate in the planning process, leading to shared ownership of the product vision and building consensus within the team. This shared understanding enhances cooperation and promotes a unified approach to product development.
Clear Priorities and Connection between Items
Through the visual roadmap and prioritized stories, User Story Mapping establishes clear priorities for the team, making it easier to make decisions about what to work on next. Moreover, it highlights the connections and dependencies between different items in the product backlog, aiding better project planning.
Built-in User Journey and Context
User Story Mapping ensures that the user journey and context are at the core of the development process. By mapping out user stories in the context of the overall product experience, teams can create a more user-centric and seamless product.
Visible Product Goals and Vision
The visual representation of the user story map provides a tangible and accessible depiction of the product goals and vision. This helps align the team around a shared purpose and drives them toward the common objective.
Helps Avoid Backlog Grooming
With a well-structured user story map and clear priorities, User Story Mapping reduces the need for frequent backlog grooming. The organized backlog allows the team to focus on developing valuable features rather than continually reevaluating and re-prioritizing tasks.
Improved Communication in the Team
User Story Mapping enhances communication and collaboration within the team. By providing a clear, shared understanding of the product development process, team members can work more cohesively, leading to more effective decision-making and problem-solving.
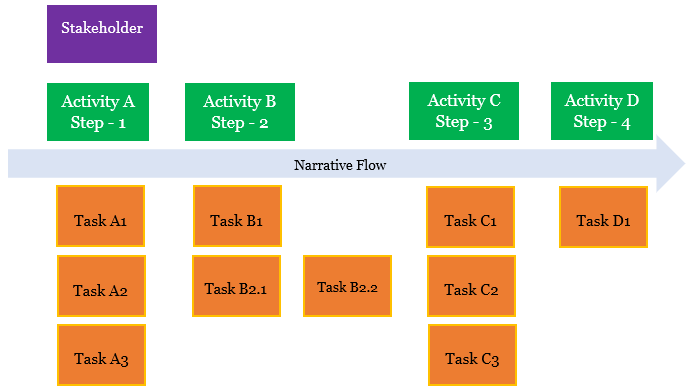
Participants in User Story Mapping
User Story Mapping is a collaborative technique that involves different stakeholders from cross-functional teams. The active involvement of various participants ensures a holistic approach to product development.
Collaborative Nature
User Story Mapping is a collaborative process that brings together team members from different disciplines to create a shared understanding of the product.
Cross-Functional Teams’ Involvement
The success of User Story Mapping relies on the participation of cross-functional teams, including engineering, UX, product management, and others.
Representation from Different Teams (Engineering, UX, Product, etc.)
By involving representatives from different teams, User Story Mapping ensures that all perspectives are considered during the mapping process.
Challenges of User Story Mapping
While User Story Mapping offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for effective implementation.
Importance of Knowing the Customer for Effective Mapping
Knowing the customer’s needs and pain points is essential for creating an accurate and valuable user story map.
The Necessity of Understanding the Problem for Accurate Mapping
Without a deep understanding of the problem and user interactions, the user story map may not align with the product’s goals.
Addressing Challenges in Physical User Story Map
A physical user story map may face challenges related to space constraints and the need for distributed teams to collaborate effectively.
Dealing with Re-Work and Redundancy in Backlog Creation
Inadequate mapping or lack of clarity may lead to re-work and redundancy in the backlog creation process.

Completion of User Story Mapping
After User Story Mapping, the team schedules prioritized stories into sprints and releases, shares the map with relevant teams for alignment and feedback, continuously updates it based on research, and uses it as a visual roadmap for future work.
Scheduling Prioritized Stories into Sprints and Releases
After prioritizing user stories, they are scheduled into development sprints and product releases to efficiently manage workload and deliver incremental value.
Sharing and Reviewing the User Story Map with Relevant Teams
The user story map is shared with relevant teams for transparency and collaboration, allowing valuable feedback and insights.
Updating the Story Map with Research and Feedback
Continuously updating the user story maps based on user research and feedback ensures it remains relevant and aligned with evolving priorities.
Utilizing Story Map as a Visual Roadmap for Future Work
The completed user story maps serve as a visual roadmap, guiding the team toward product goals and facilitating effective communication with stakeholders.
Conclusion
User Story Mapping is an essential tool for modern product management and development. Its ability to focus on user value, prioritize work, and build a shared understanding among teams makes it a powerful technique. By following the steps outlined in this article, business analysts and product owners can leverage User Story Mapping to drive successful product development. Remember to continuously improve and maintain empathy towards customers to make the most of this efficient approach.
FAQs
What is story mapping in business analysis?
Story mapping in business analysis is a collaborative technique used to visually represent the user journey and product features. It involves breaking down complex ideas into smaller user stories, which are then prioritized based on user value and feasibility. Story mapping helps build a shared understanding among team members and ensures a user-centric approach to product development.
How do you write user story maps?
To write user story maps, start by understanding the target audience and defining user personas. Then, identify user activities and break them down into smaller user story maps. Prioritize the stories based on user value and feasibility, creating a coherent roadmap. Continuously update the map based on research and feedback to keep it relevant.
Who facilitates user story mapping?
User story mapping is typically facilitated by a facilitator who guides the collaborative process. The facilitator can be a business analyst, product owner, or any team member with experience in Agile methodologies. Their role is to ensure that all participants are engaged, that discussions stay on track, and that the map accurately reflects the team’s decisions.
How do you create a product management story map?
To create a product management story map, start by defining clear product goals and understanding the target audience. Gather input from various stakeholders and cross-functional teams. Map out the user journey and prioritize features based on user value and business objectives. Continuously update the story map based on user feedback and market changes to ensure the product remains relevant and competitive.



